Mobile System Design Guide
21 October 2024
Before building a product, we need to set some requirements, architecture designs, security concerns etc. These play an important role in organizing, creating fast and scalable applications. A typical mobile system design includes application features, architecture design, and out-of-scope requirements like crash reporting, analytics etc.
In Mobile System Design sessions, the interviewer wants to understand the candidate’s thought process, problem-solving abilities, architecture design solutions, and handling of edge cases. It’s always better to gather the ground before you start. You should start with simple questions and ask as much as you can.
I’ve seen multiple candidates in interviews start their introduction and end up with 5–6 minutes. It’s recommended to have a short introduction about yourself. For example: “I’m X working on Android/iOS applications and libraries since 2020. For the past 2 years, I’ve been leading a team of X product used for messaging.” A typical system design interview should be 40–45 minutes, split into High-level design (20 mins) and Low-level design (20 mins).
Information Gathering
After the introduction, it’s recommended to start with information gathering by asking questions. However, you should be careful not to ask for solutions every time. Instead, ask for requirements and provide solutions. Indeed, the interviewer wants to understand the candidate’s thought process. In general, information gathering is divided into 4 aspects:
- Functional Requirements
- Non-Functional Requirements
- Out of Scope
- Resources
Functional Requirements
Functional requirements are the features or screens that are immediately visible to the user while navigating the application. For example:
- User able to scroll through messages
- User able to send messages
- User able to send attachments/photos
- User able to delete a message
Non-Functional Requirements
Non-functional requirements play an important role in making the application more stable and scalable. For example:
- Realtime notifications
- Realtime Sync
- Offline Support
- CPU/Battery Optimizations
Out of Scope
Additional requirements different from features that play an important role in the application:
- Analytics
- Crash Reporting
- Remote Logging
- Performance
- Accessibility
- Security
Resources
Resources include additional requirement gathering like team size, locale, number of users etc. While gathering resource information, you can ask questions like:
How big is the engineering team?
Building a product for a small team is always different from a product designed for a large team. A large team’s product is more structured and modularized to scale and better manage the product.
What is the expected number of total users?
A large number of users is expected to create server load. This question might make sense while managing the API clients and server-side issues.
Are we targeting a specific area like India?
This question might make sense while designing the product for different internet connectivity areas. A low internet connectivity area requires minimum API connections to reduce bandwidth.
High Level Design
Before you move into high-level design, ask your interviewer: “Should I start with High-level design or Low-level design?” High-level design includes a typical product structure like modules with exposing the internal communication. Low-level design explains the internal communication between the modules or features.
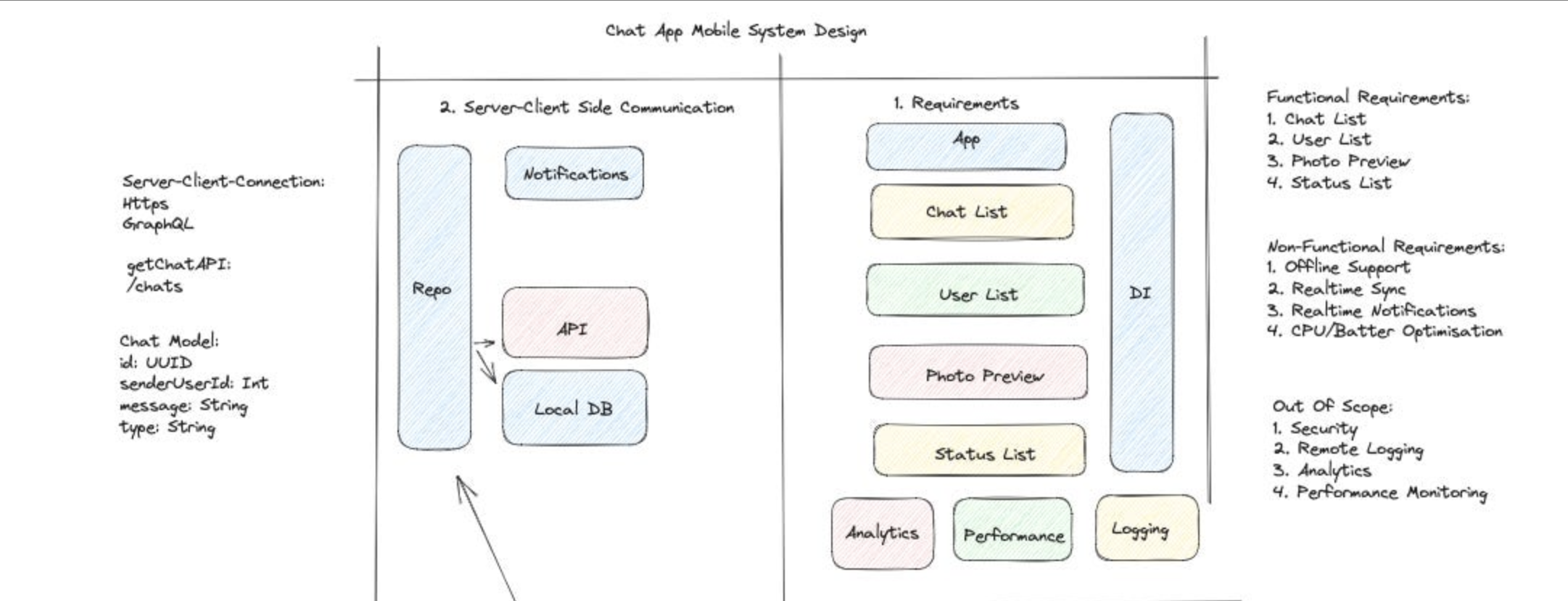
How to approach the high-level design?
At first glance, it’s recommended to start with features, server-client communication, models, then come down to low system design. Let’s understand this one by one:
- Functional Requirements
- What features are required?
- Client-Server Communication
Define the communication frameworks like HTTPS, WebSocket, Nats, HTTPS Polling etc.
- Which one should be used — HTTPS, GraphQL etc.?
- Why choose Nats over WebSocket?
- What are the disadvantages of using HTTP Polling?
- What are the advantages of using WebSocket?
-
API Design Define the API used to implement the feature on server client. For instance, fetching the chat list using
/chatsAPI. - Data Models
Define the data models:
- Draw and choose the properties inside data model
- Can we have a list inside a data model that will be stored in the local database?
-
Repository, Local and Network Define the communication between repository, local database and network data source.
- Non-Functional Requirements
Explain how to manage non-functional requirements like realtime sync, realtime notifications etc:
- What are the disadvantages of using server-side notifications?
- What are the issues caused during realtime sync? And how to deal with them?
- How to handle cache?
Low Level Design
After diving into high-level design, let’s try to understand the low-level design or app flow. It’s recommended to start the deep dive session after getting the signal from the interviewer. Low-level design or deep dive session includes architecture design, state, screen etc.
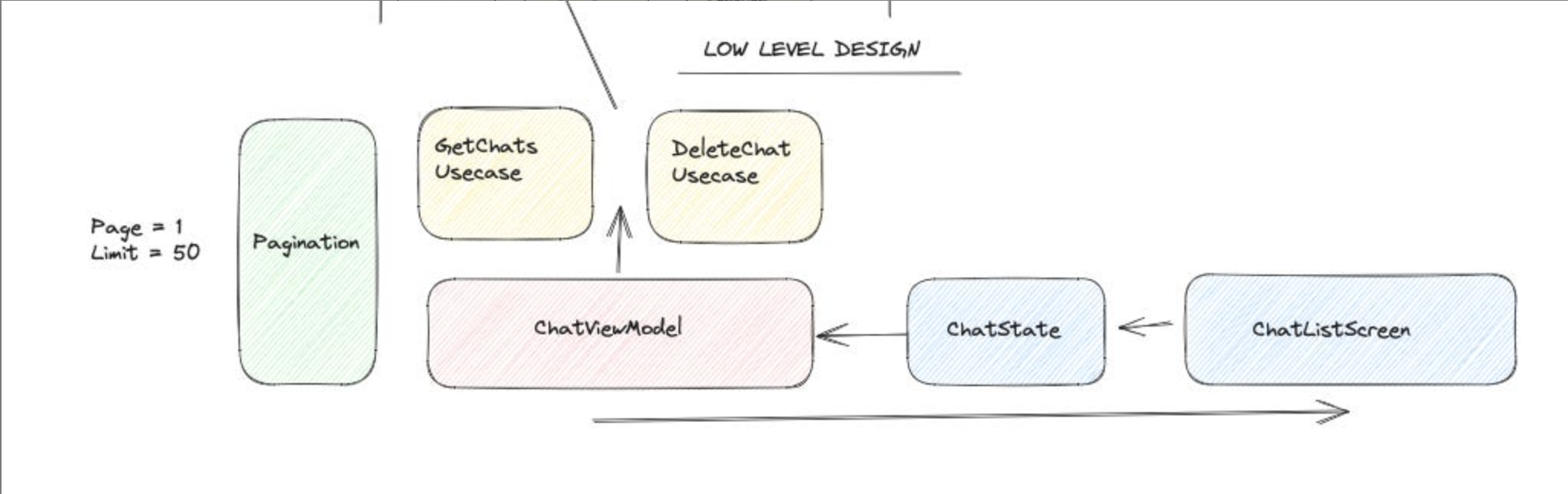
How to approach the low-level design?
- Architecture
Define the architecture design that should be followed according to application requirements:
- Why choose MVVM over MVC?
- Dependency Injection
Define the dependency injection:
- Why do we need dependency injection?
-
Pagination or Remote Mediator Define how pagination will work.
-
Usecase Define the usecase which is responsible for reducing the complexity of business logic.
-
ViewModel & State Define the ViewModel and its usages if we are following the MVVM architecture. For instance, how will the screen or UI communicate with the ViewModel?
- Out of Scope
Explain the out-of-scope requirements:
- How to secure the application?
- How to gather data like events and use as analytics?
- Explain Security practices
- What are the advantages of using Analytics?
- Performance
Define the performance matrix:
- How will large images affect scrolling performance?
- How will threading affect performance?
- How to load large amounts of data?
- Accessibility
Define the accessibility:
- How will UI component sizing and colors affect users?
- How will color contrast and small text size affect some users?
-
Localization Define the localization. Localization means enabling local languages in the application to make it more usable.
- Security
Define the security matrix:
- How to secure secret keys like API Keys?
- How to secure local backup or local database data?
- How will app permissions affect security measures?
- How to encrypt data?
And here we are done! Thanks for reading!